Accessible Low-Code, No-Code Development

Wiktoria Drezner
LinkedIn Länk till annan webbplats, öppnas i nytt fönster.
Emmanuel Edigbe
Analysing the Accessibility of Websites Built with Low-Code and No-Code Technologies in the Citizen Developer Context
The job market has shifted towards low-code and no-code solutions, with companies training business professionals as citizen developers. This trend raises concerns about whether websites created by non-professionals meet web accessibility standards.
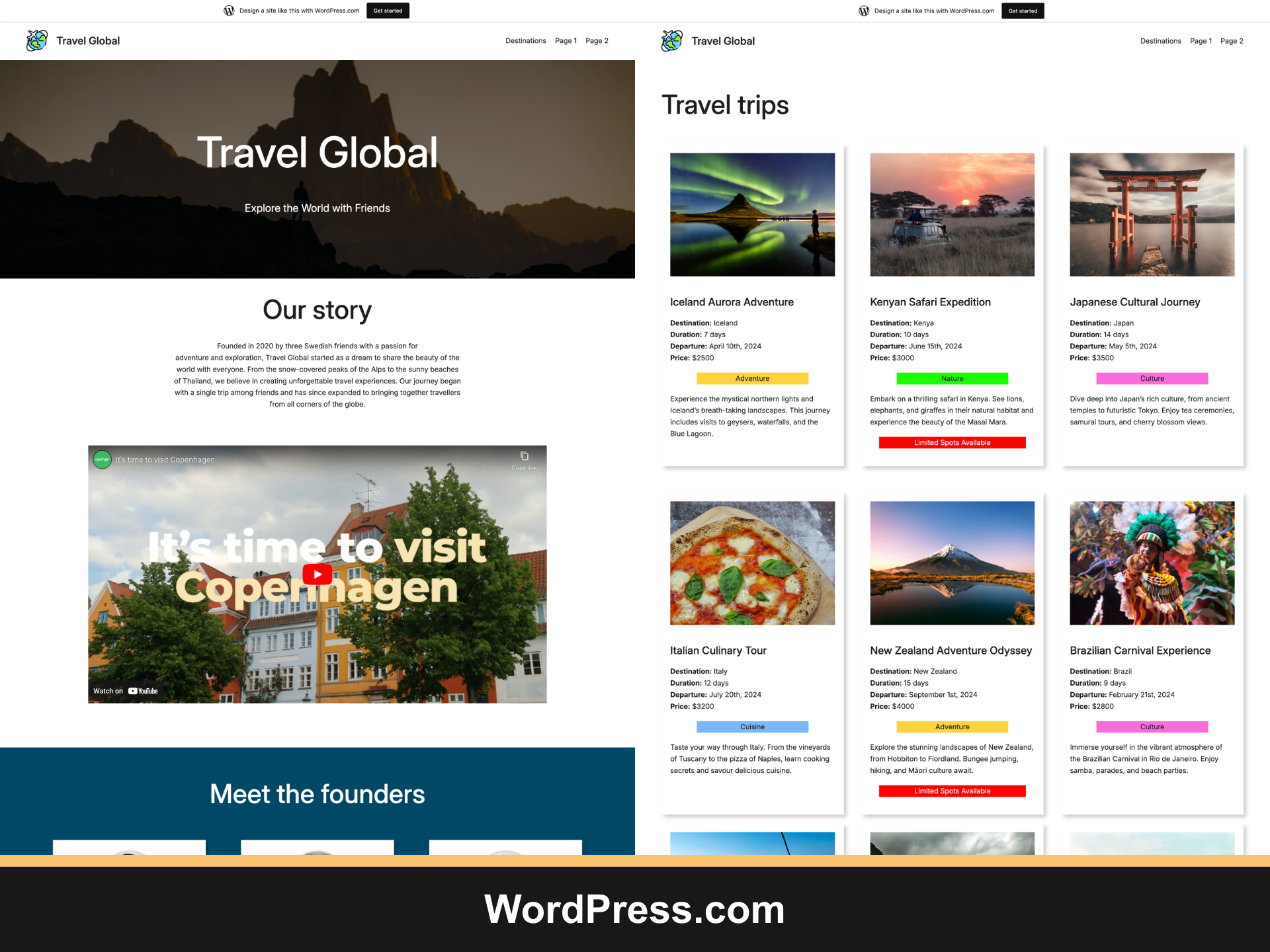
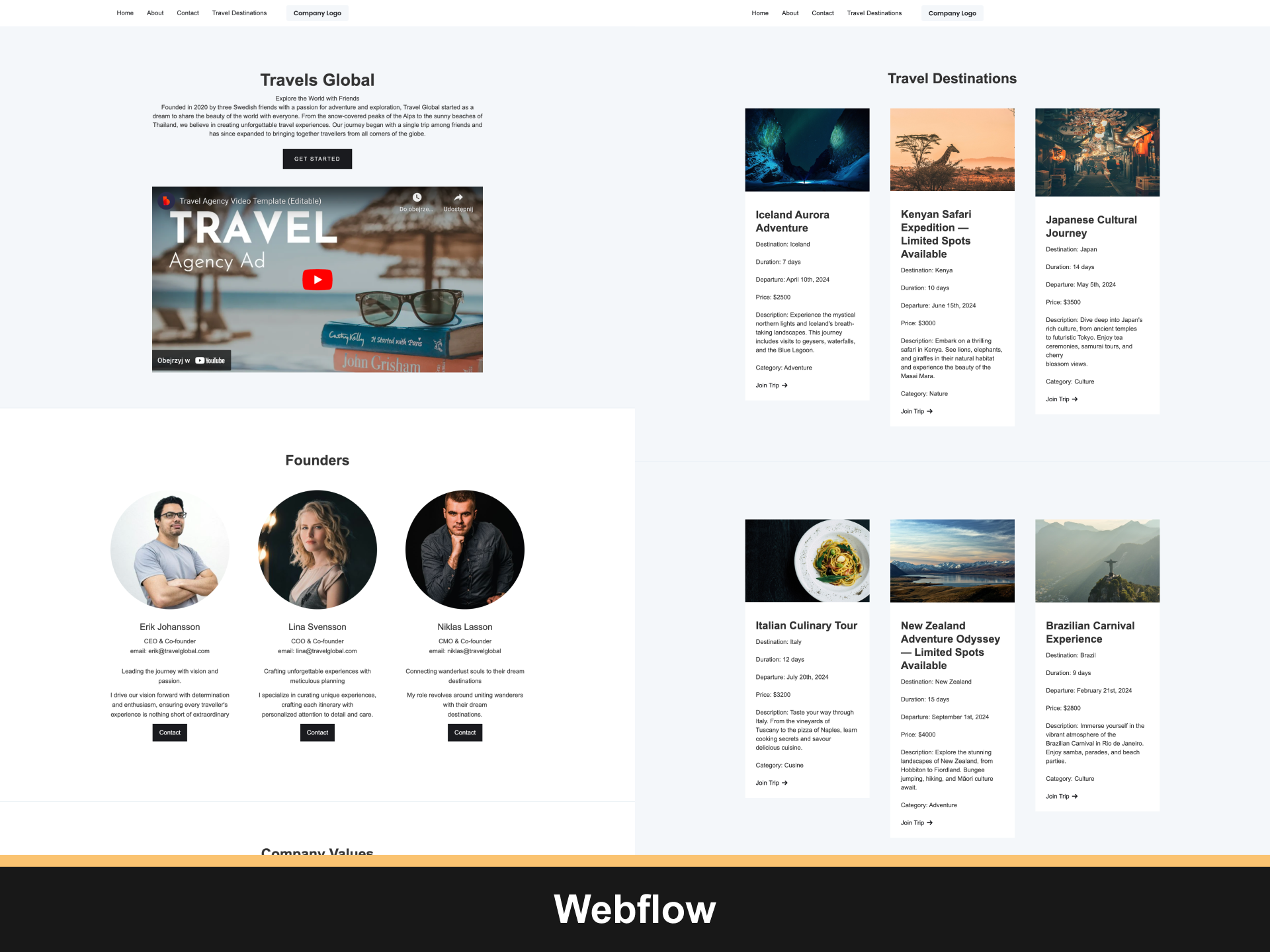
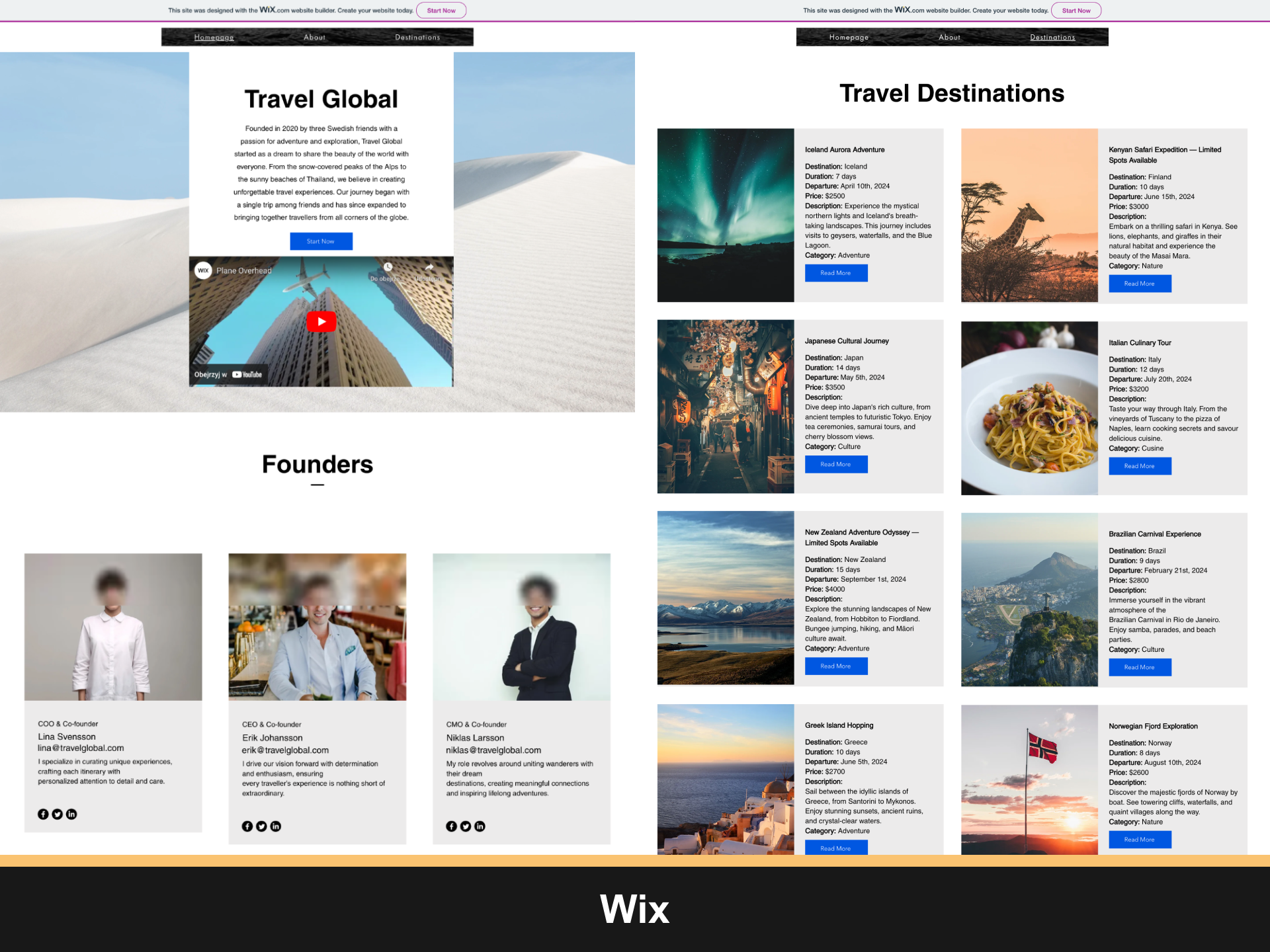
Our study investigates the phenomenon and spans results across three areas: the extent of compliance with accessibility guidelines (1), prevalent accessibility challenges (2), and optimal practices for accessibility enhancement (3). The research involves tasking five individuals with creating websites using different low-code and no-code tools. Then, the websites are objectively evaluated for accessibility adherence using Google Lighthouse Analytics and WCAG 2.2 criteria assessment.
The research concludes that websites developed by citizen developers do not meet accessibility standards. Many websites struggle with the fundamental aspects of accessibility that are necessary for pleasant and comfortable use. To improve the situation, web developers—professionals and amateurs—should prioritise accessibility in web development and design.